Examples
Block World Problem
In this problem, we require the LLM to generate a plan to control a robotic arm to stack blocks on a plane as specified.
Fill in your gpt api key in the file case1/auto.py. Then in the case1 directory, run the following command to start the tool.
python auto.py
The tool reads the prompt from first_prompt_formula.txt and instructs the LLM to generate FOL specifications in the format required by the Z3 Python API.
After manually checking the correctness of the generated specification, we proceed to request the LLM to generate a plan using prompt from first_prompt_plan.txt.
Important
You can find the correct specification code in case1/draft.py for this example.
The specific problem is as follows.
(define (problem BW-rand-6)
(:domain blocksworld-4ops)
(:objects b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 )
(:init
(arm-empty)
(on b1 b6)
(on b2 b3)
(on-table b3)
(on b4 b1)
(on-table b5)
(on-table b6)
(clear b2)
(clear b4)
(clear b5)
)
(:goal
(and
(on b1 b2)
(on b5 b3)
(on b6 b4))
)
)
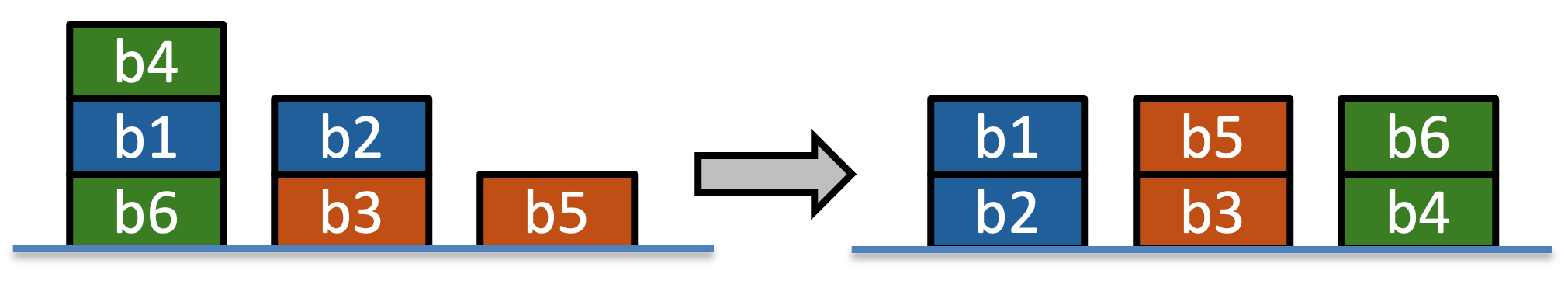
The figure below shows the initial state and the goal state of the problem.
The first plan generated by LLM is shown below.
START-PLAN
1. pick-up b5
2. stack b5 b3
3. unstack b1 b6
4. put-down b1
5. pick-up b6
6. stack b6 b4
7. pick-up b2
8. stack b2 b1
END-PLAN
After customizing the verifier (inherited from class Fol_verifier) based on the task, the plan is verified against the specification, and the reasoning is provided as follows.
The plan is invalid according to the steps below.
1. pick-up b5
2. stack b5 b3
The reasoning is passed as a new prompt to the LLM to generate a revised plan, which is then verified again. This process continues until a plan that satisfies the specification is obtained or the user-defined iteration limit is reached.
Correct result is shown below.
START-PLAN
1. unstack b4 b1
2. put-down b4
3. unstack b1 b6
4. put-down b1
5. pick-up b6
6. stack b6 b4
7. unstack b2 b3
8. put-down b2
9. pick-up b5
10. stack b5 b3
11. pick-up b1
12. stack b1 b2
END-PLAN